Polymerization Inhibitor 510 ——Making Your UV Coatings More Stable and Efficient
Today, let's talk about polymerization inhibitors. Polymerization inhibitors are additives used to inhibit the polymerization reaction in UV - formulated products. They can extend the storage time of olefin resins and are suitable for UV inks, UV coatings, UV adhesives, photoresists, unsaturated polyester resins, vinyl monomers, acrylate oligomers, etc.
I. What are the traditional polymerization inhibitors?
1. Hydroquinone
★ Features: It is a highly efficient polymerization inhibitor that can effectively extend the storage period and prevent pre - polymerization.
★ Applications: Widely used in various UV coatings, especially in highly reactive systems.
2. Methoxyhydroquinone
★ Features: It is more stable than hydroquinone and has a better polymerization - inhibiting effect.
★ Applications: Suitable for high - demand UV coatings, such as high - gloss and weather - resistant coatings.
3. 2,6 - Di - tert - butyl - p - cresol (BHT)
★ Features: It has strong antioxidant properties and can prevent pre - polymerization caused by oxidation.
★ Applications: Commonly used in UV coatings that need long - term storage.
4. Phenothiazine
★ Features: It is a highly efficient polymerization inhibitor, especially suitable for highly reactive monomers.
★ Applications: Mostly used in highly reactive UV coatings, such as fast - curing systems.
5. Benzoquinone
★ Features: It has a strong polymerization - inhibiting effect, but the dosage needs to be controlled. Excessive use will affect curing.
★ Applications: Used in UV coatings where the polymerization rate needs to be strictly controlled.
6. Nitrobenzene
★ Features: It has a significant polymerization - inhibiting effect, but it has certain toxicity.
★ Applications: Used in industrial UV coatings, and safe operation should be noted.
7. Xanthone
★ Features: It has good light stability and is suitable for photocuring systems.
★ Applications: Used in UV coatings with high requirements for light stability.
8. Triphenylphosphine
★ Features: It has both polymerization - inhibiting and catalytic effects and is suitable for complex systems.
★ Applications: Used in multi - functional UV coatings, such as occasions where both polymerization inhibition and catalysis are required.
II. The Emergence of High - end Polymerization Inhibitor 510
Polymerization inhibitor 510 : Aluminum N-Nitroso-N-phenylhydroxylamine
Its structural formula is as shown below:
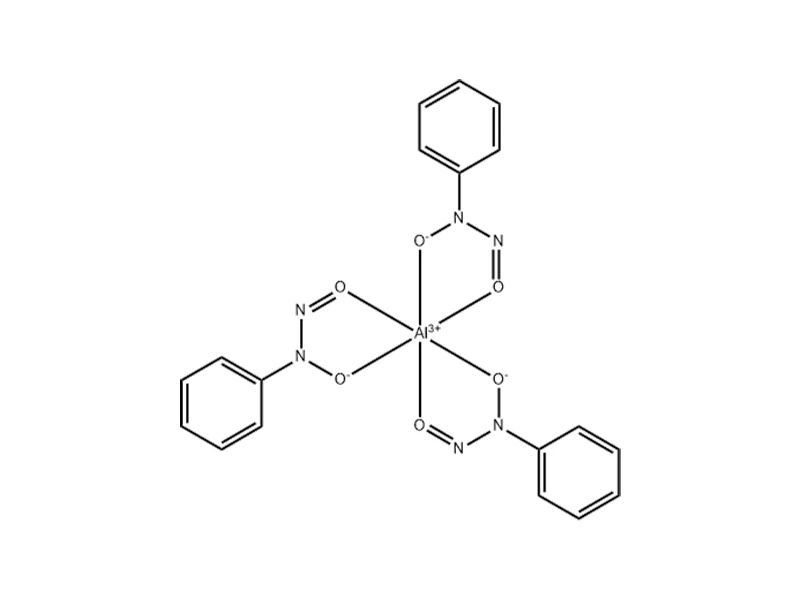
III. The Secret of the Polymerization - Inhibiting Principle of 510
1. Free - Radical Trapping Mechanism
This compound can effectively trap free radicals in the system, preventing the polymerization reaction initiated by free radicals.
Free - radical - nitroxide radicals generate stable inactive molecules by decomposing peroxides, which can effectively trap active chain free radicals and enhance the anti - polymerization effect. At the same time, the introduction of oxygen can significantly increase the activity of nitrate compounds, thereby inhibiting their activity.
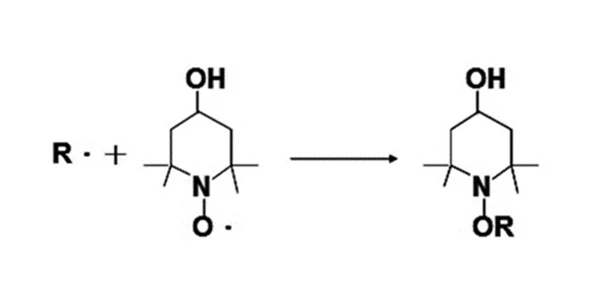
During the UV curing process, free radicals are the key to initiating monomer polymerization. Trapping free radicals can delay or prevent polymerization.
2. Stabilization Effect
Through the stabilization effect, it prevents pre - polymerization and premature reactions during storage. During storage and use, the polymerization inhibitor can keep the system stable and prevent pre - polymerization caused by temperature or light.
3. Light Stability
This compound is relatively stable under light and does not easily decompose to generate free radicals. During the UV curing process, the polymerization inhibitor will not lose its effectiveness due to light, ensuring that it can still play a polymerization - inhibiting role when needed.
4. Synergistic Effect
It works synergistically with other additives to enhance the polymerization - inhibiting effect. In complex formulations, it synergizes with other stabilizers or antioxidants to provide more comprehensive polymerization - inhibiting protection.
Ⅳ. Advantages over Traditional Polymerization Inhibitors
1. ★ Higher Efficiency:
Compared with traditional polymerization inhibitors such as hydroquinone, polymerization inhibitor 510 has a stronger free - radical - trapping ability and a more significant polymerization - inhibiting effect.
2. ★ Wider Applicability:
Whether it is highly reactive monomers or complex formulations, polymerization inhibitor 510 can be perfectly adapted, while traditional polymerization inhibitors may be limited by system compatibility.
3. ★ Better Stability:
Under light and high - temperature environments, polymerization inhibitor 510 performs more stably, avoiding the problem of traditional polymerization inhibitors losing their effectiveness due to decomposition.
4. ★ More Environmentally Friendly and Safe:
With low toxicity and environmental - friendly characteristics, it meets the needs of modern industry for green chemicals.
If you are interested in polymerization inhibitor 510, please feel free to contact us.
Send a private message with "Polymerization Inhibitor 510" or "YS - 510" to obtain detailed product information.





