In-depth Discussion on Printing Equipment for UV-curable Inkjet Technology
UV-curable inkjet inks have seen increasingly widely used in the industrial printing field, owing to their high curing efficiency, environmental benignity, and excellent adhesion. This series of articles will systematically analyze the core links of UV-curable inkjet technology: first, it will interpret inkjet printing equipment; second, it will conduct an in-depth discussion on the technical difficulties of ink formulations; finally, it will analyze the performance requirements and innovation trends of key raw materials.
By integrating theory with practice, this (series of articles/analysis) provides technical references for industry practitioners and facilitates product development and process upgrading. Today, we will start by gaining an understanding of inkjet printing and inkjet devices.
Inkjet printing is a non-contact, pressure-free, and plate-free printing method. Composed of a system controller, inkjet controller, printhead, and substrate drive mechanism (among other components), it works by editing graphics and text on a computer, which then controls the printhead of the inkjet printer to eject ink droplets onto the substrate, resulting in precise images. This constitutes an entirely digital printing process.
As a product of the integration of digital printing technology and computer technology, inkjet printing has become one of the fastest-growing and most widely used printing methods in the field of digital printing.
Currently, there are two main types of inkjet printing: thermal inkjet and piezoelectric inkjet.
✿ Thermal Inkjet Device: Composition and Working Principle
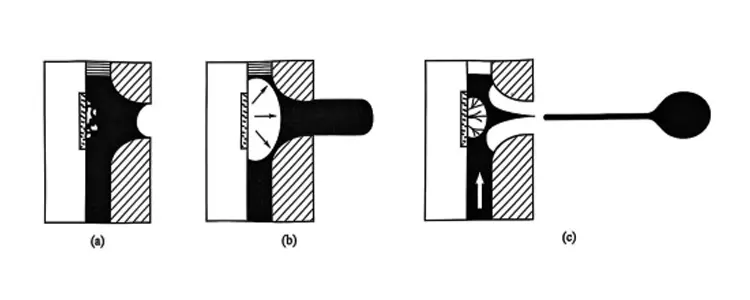
A thermal inkjet device consists of an ink chamber, a printhead, and a heater. The heater, which is a thin-film resistor, heats the ink in the ink ejection area to form a bubble. This bubble expands and bursts instantaneously, ejecting the ink from the printhead. The entire process of bubble formation and burst takes less than 10 microseconds (μs). Subsequently, the ink refills the ink chamber, preparing for the next cycle. (See the figure below for a schematic diagram of the thermal inkjet process)
✿ Piezoelectric Inkjet Device: Composition, Working Principle and Application Advantages
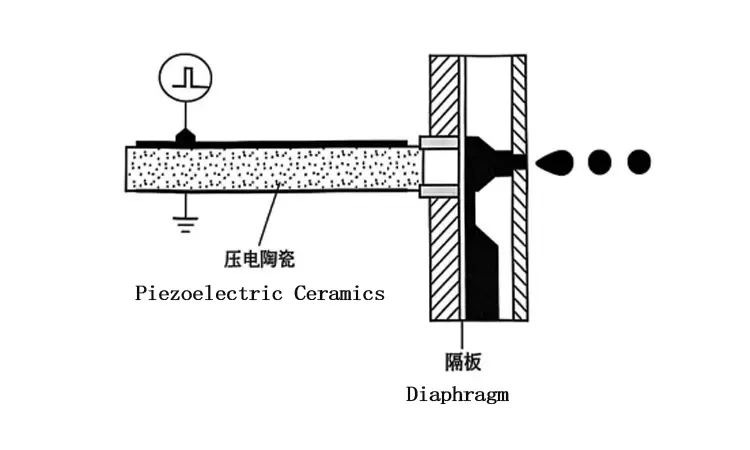
A piezoelectric inkjet device is composed of a piezoelectric ceramic, a diaphragm, a pressure chamber, and a printhead. When a voltage is applied to the piezoelectric ceramic, it deforms, causing a change in the volume of ink within the pressure chamber. This volume change generates high pressure, which ejects the ink from the printhead.
Currently, piezoelectric inkjet technology offers several advantages: faster ink ejection speed, easier control over the shape and size of ink droplets, and a longer printhead lifespan. Additionally, it is compatible with various types of inkjet inks. Although the initial cost of piezoelectric inkjet equipment is slightly higher, its operational cost is low. For these reasons, large-format inkjet printers all adopt piezoelectric inkjet technology. (See the figure below for a schematic diagram of the piezoelectric inkjet process)
Substrate Versatility of Inkjet Printing
Inkjet printing can be applied to a wide range of substrates, including paper, cardboard, films, plastics, metals, wood, ceramics, glass, fabrics, and leather. It is no exaggeration to say that current inkjet imaging technology can print on almost all flat and non-flat substrates—with the only exceptions being water and air.
Now that we have gained an understanding of the inkjet process, we will delve into the preparation of UV inkjet inks in the next article.
If you have any product requirements or technical inquiries, please feel free to contact us at any time. We look forward to cooperating with you!





