The Niche Photoinitiator 2-EAQ: Analysis of Properties and Applications
Abstract:
This article will introduce 2-EAQ (2-ethylanthraquinone), a relatively niche photoinitiator, focusing on its chemical properties and unique application advantages in the field of photocuring. It will also analyze its current market situation and precautions during use, so as to provide references for practitioners in related industries.
2-ethylanthraquinone (abbreviated as 2-EAQ) is an important organic compound, which is used in the production of hydrogen peroxide, dye intermediates, photocurable resin catalysts, photodegradable films, coatings, and photosensitive polymerization initiators, etc. Today, we will mainly discuss its application in the field of photocuring.
1. Product Information
✿ Product Structure:
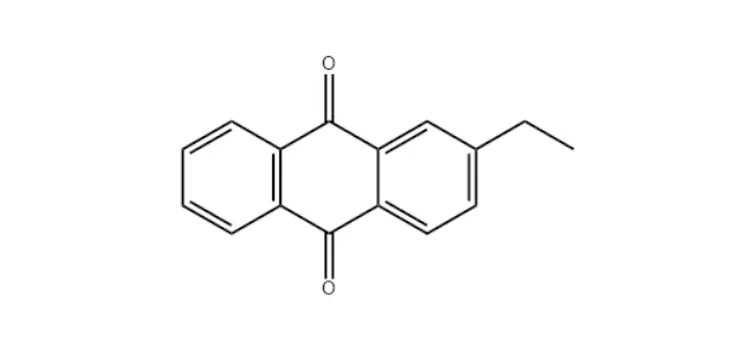
✿ Appearance: Light yellow to yellow crystalline flakes or powder
✿ Purity (HPLC): ≥98.00%
✿ Melting Range: 108~111 ºC
✿ Absorption Peaks: 256nm, 275nm, 325nm; the absorption wavelength can reach 430nm, which falls into the visible light absorption region.
2. Principle of Photocuring Reaction
After absorbing light energy, 2-EAQ interacts with the co-initiator tertiary amine in its excited triplet state. Through hydrogen abstraction, it generates two types of free radicals: phenoxyl radicals (A) with no initiating activity, and aminoalkyl free radicals with high initiating efficiency. The latter initiates the polymerization and cross-linking reactions of oligomers and reactive diluents.
Subsequently, the phenoxyl radicals undergo bimolecular disproportionation to form 9,10-anthrahydroquinone (B) and 2-EAQ. Both the phenoxyl radicals and anthrahydroquinone can be oxidized by O₂, and both reactions regenerate 2-EAQ. Therefore, under aerobic conditions, the efficiency of the photoinitiator is higher than that under anaerobic conditions; in other words, 2-EAQ exhibits low sensitivity to oxygen inhibition in polymerization.
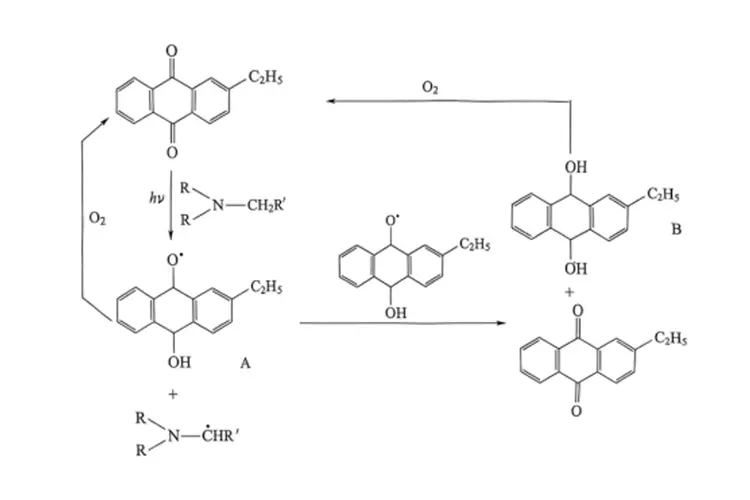
Although 2-EAQ shows low sensitivity to oxygen inhibition in polymerization, its intermediate products—phenoxyl radicals and anthrahydroquinone—are both inhibitors of free radical polymerization. Consequently, the photoinitiating activity of anthraquinone-based compounds (including 2-EAQ) is relatively low.
2-Ethylanthraquinone (2-EAQ) is mainly used in the solder mask ink of PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards).
When exposed to UV light,, it initiates cross-linking reactions to form a cured layer that is resistant to etching or soldering.
3. Advantages of 2-EAQ in Solder Mask
✿ Heat Resistance (Solder Temperature Resistance):
The cured layer formed with 2-EAQ can withstand the high temperatures encountered during the soldering process of electronic products, maintaining structural and performance stability without delamination or failure, thus ensuring reliable protection of PCB circuits.
✿ Chemical Resistance (Etching Resistance, Solvent Resistance):
It enables the solder mask to exhibit excellent resistance to corrosive etching solutions (critical for preserving precise circuit patterns during PCB manufacturing) and common organic solvents, preventing swelling, dissolution, or performance degradation of the cured layer in chemical environments.
✿ Environmental Friendliness:
2-EAQ itself complies with mainstream environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH. This makes it suitable for manufacturing export-grade electronic products, helping enterprises meet global environmental compliance requirements and support the development of green electronics.
If you have any product requirements or technical inquiries, please feel free to contact us at any time. We look forward to cooperating with you!





